plan business
Structure metadata is data about an object in Phonemos that can be defined in a structured way.
Metadata can be defined either locally within a topic (see Structure your information into sites and topics) or a zone (see Zones in Phonemos: Protect & Structure) or globally to be reused in many topics.
Defining global metadata
To define globally available metadata, as a site manager go to settings and select “Configure Data Structures”.
This will bring up a list of data domains.
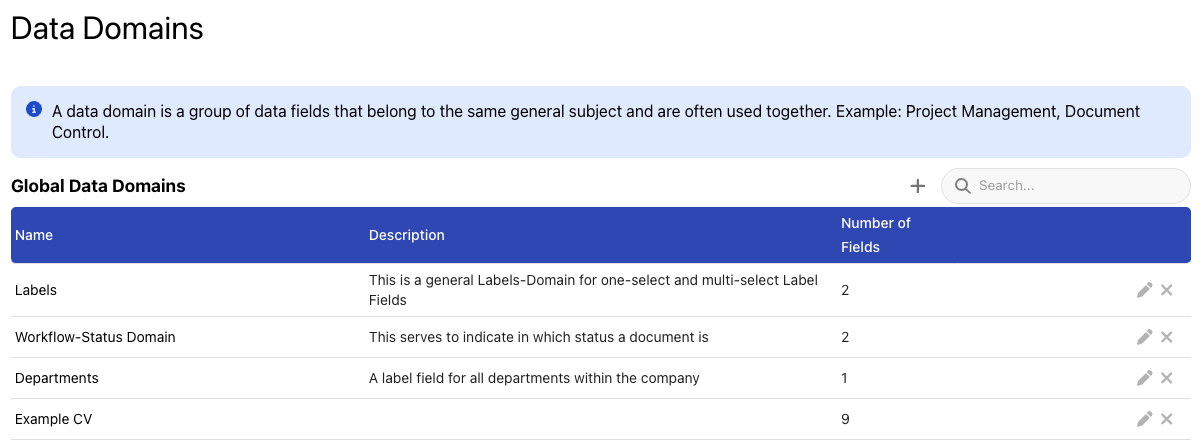
A data domain is a grouping mechanism for metadata fields. The UI will group metadata fields belonging to the same group together, but it is possible to only activate and use certain fields out of a data domain in specific topics.
Add a data domain
Select the + icon to create a new data domain.

After naming the data domain, we can add fields to it with the +-icon.
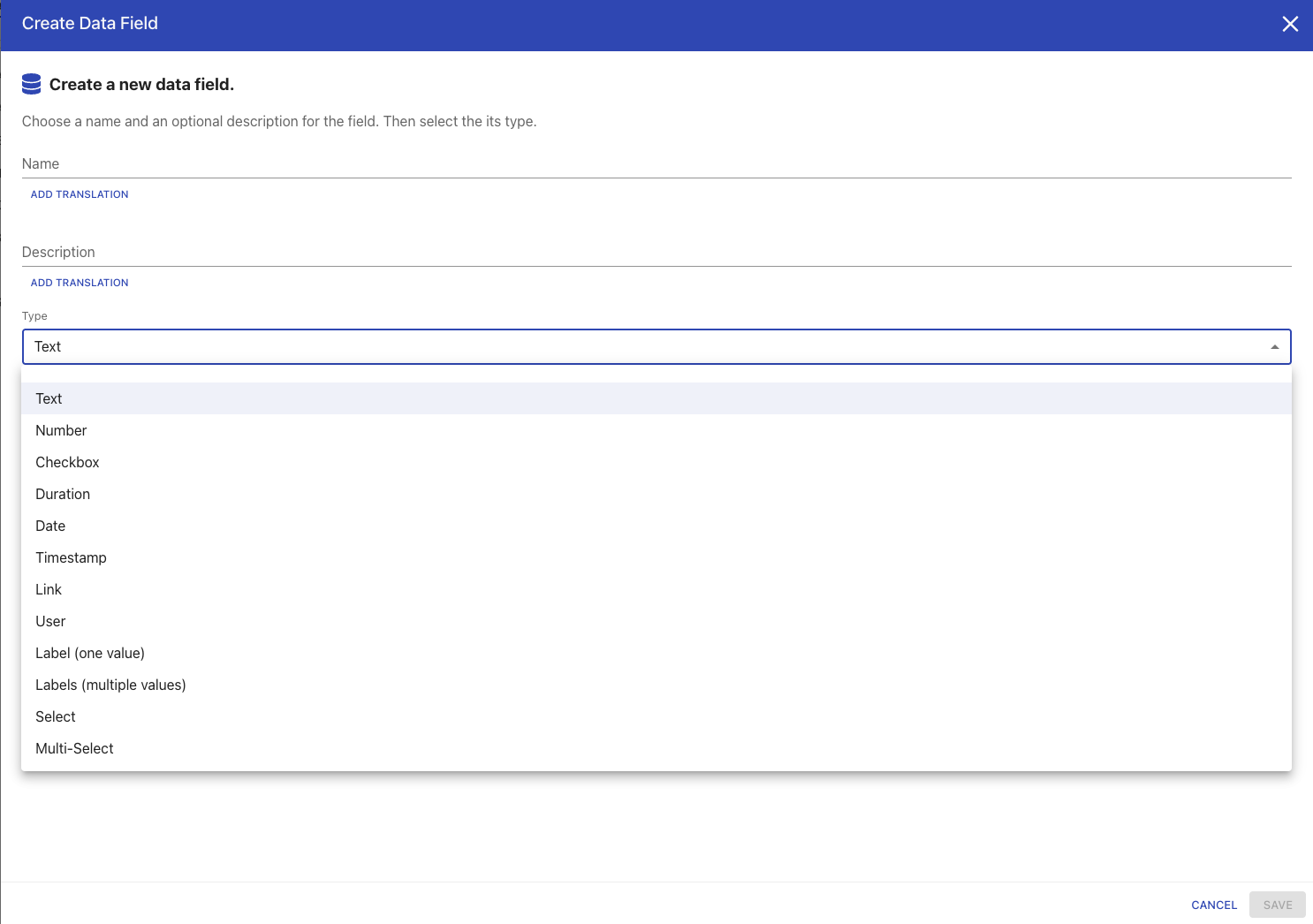
Please note that there are many different field types to choose from.
Type | Description |
|---|---|
Text | A free text field. |
Number | A number field with a detailed configuration of decimal places and units. 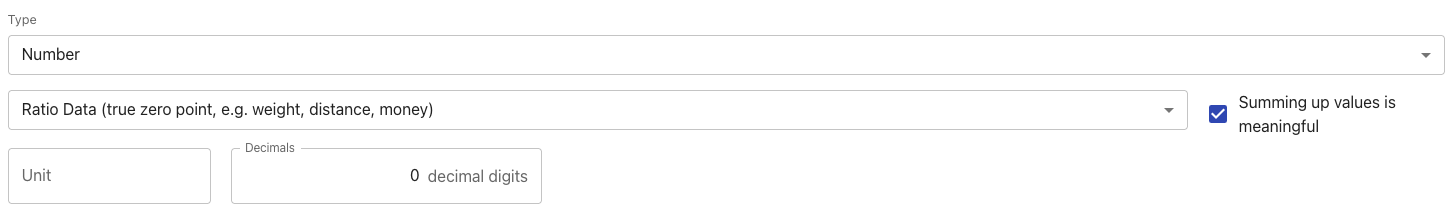 In data tables, we also perform functions on these fields like building sums and averages. If your number is a product code, summing up such an arbitrary number does not make sense. Use the checkbox to indicate whether mathematical functions produce meaningful values. |
Checkbox | Either enabled or disabled |
Duration | A special number representing time passed. 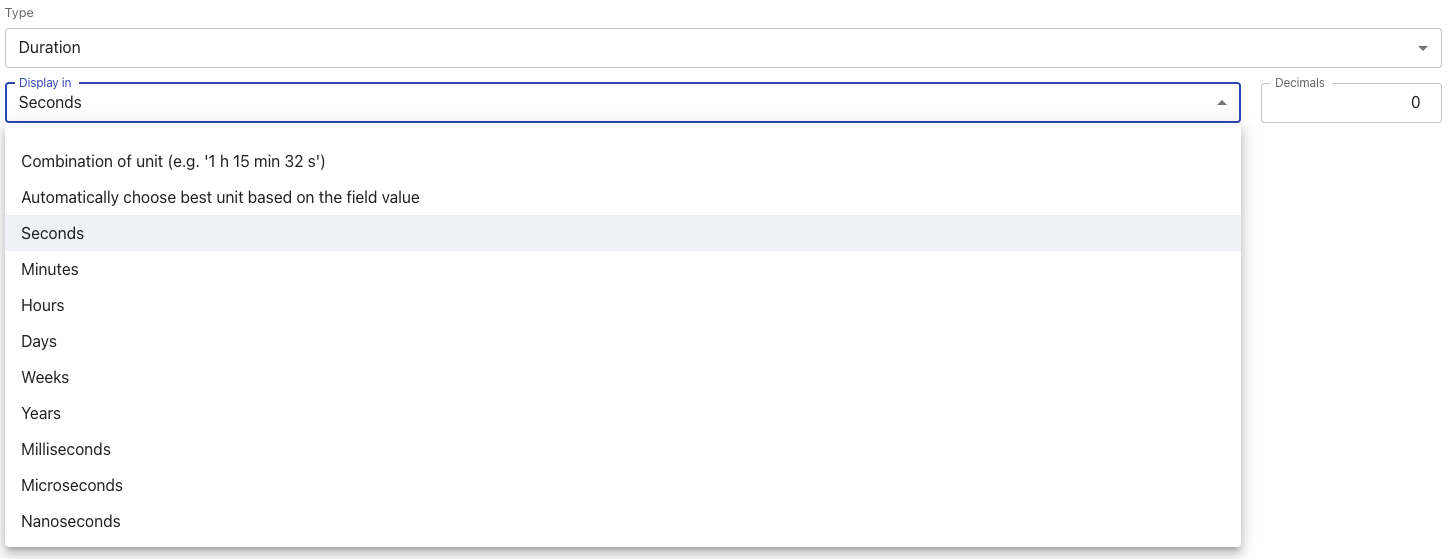 We have a specialised type for this as we can convert between units and even combine units, e.g. “1 h 15 min 32 s”. |
Date | A data, will come with a data picker widget. |
Timestamp | Combination of date and time |
Link | A link to any URL. |
User | A user name, will come with a user picker from the user directory. |
Label (one value) | Will allow people to attribute no or one label from a list of labels to this object, including adding a new label. If you don’t want people to add new labels, use the Select data type. |
Label (multiple values) | Same as the previous, but you may attribute multiple labels to every object. |
Select (one value) | Works similar to labels, but users cannot add new options, meaning there is a label cage of predefined options. In addition, you can also define colours or icons for each selection option. 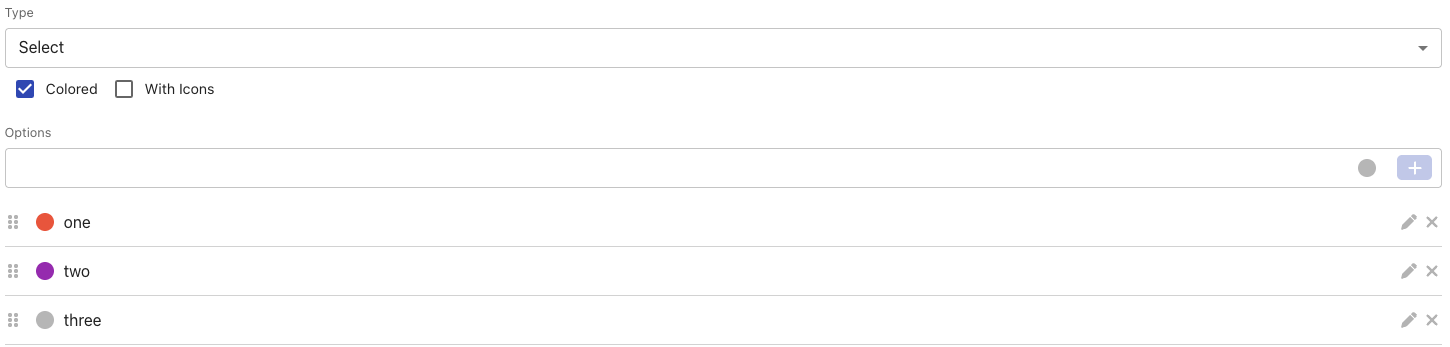
|
Select (multiple values) | Same as previous, but users can attribute several options per object. |
Activating metadata in a topic (or zone)
In the topic and zone settings, you can find the metadata section. You may add fields to activate them in your topic.
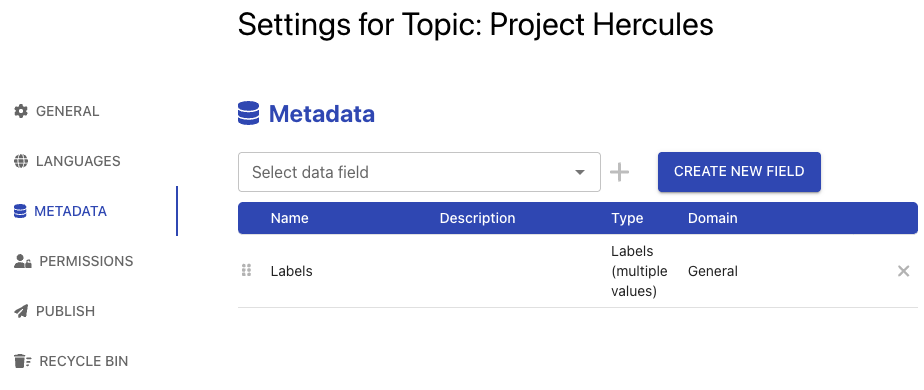
You may add more fields from the predefined data structures or add new fields for local use that cannot be shared outside of the current topic or zone context.
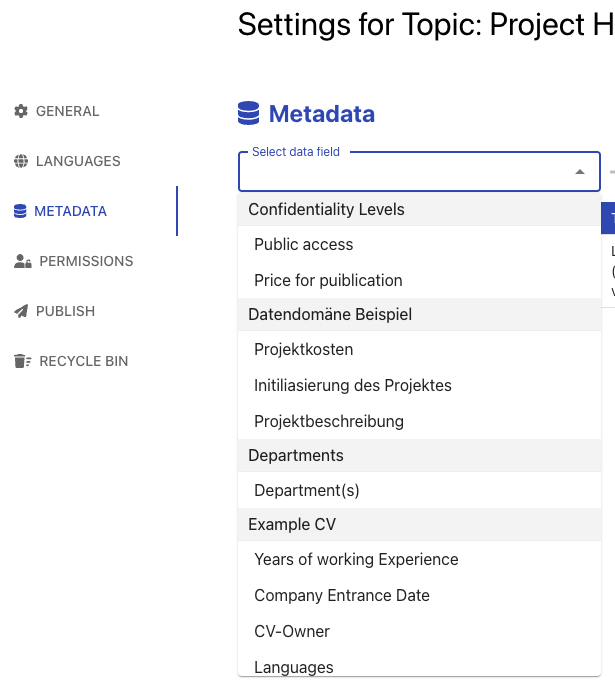
You can now use these fields to attribute metadata value to your objects. We build an example with a list of CVs of employees.
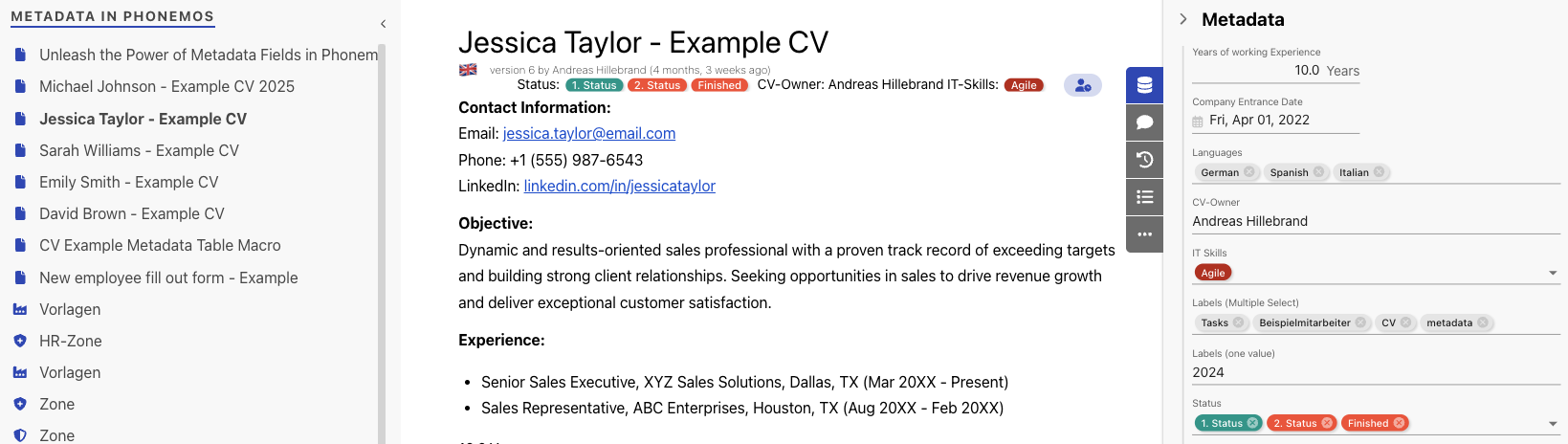
Once you have attributed a set of CVs with field values, you may use the data table to filter them and display them in a table.
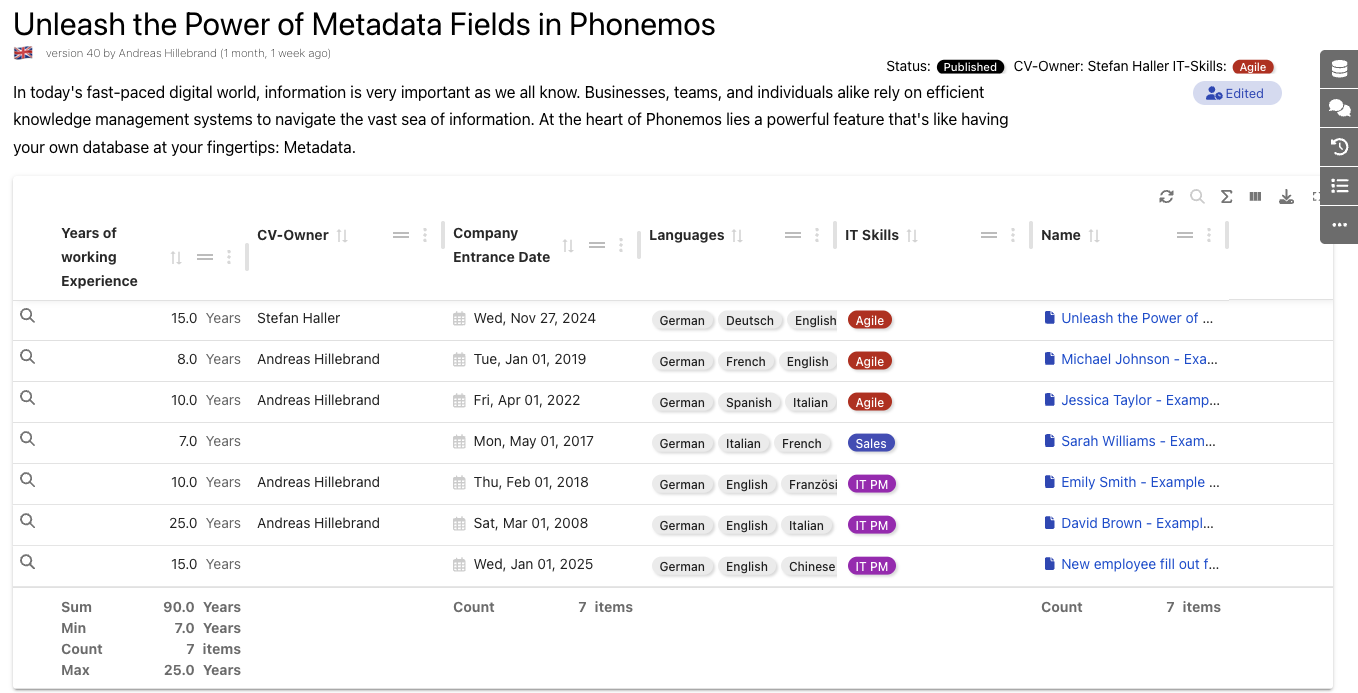
Please note that you can add mathematical functions like sum to show how many years of working experienced the employees have combined. Data tables can be sorted and grouped. In this example, we group the table by the field “IT Skills”.
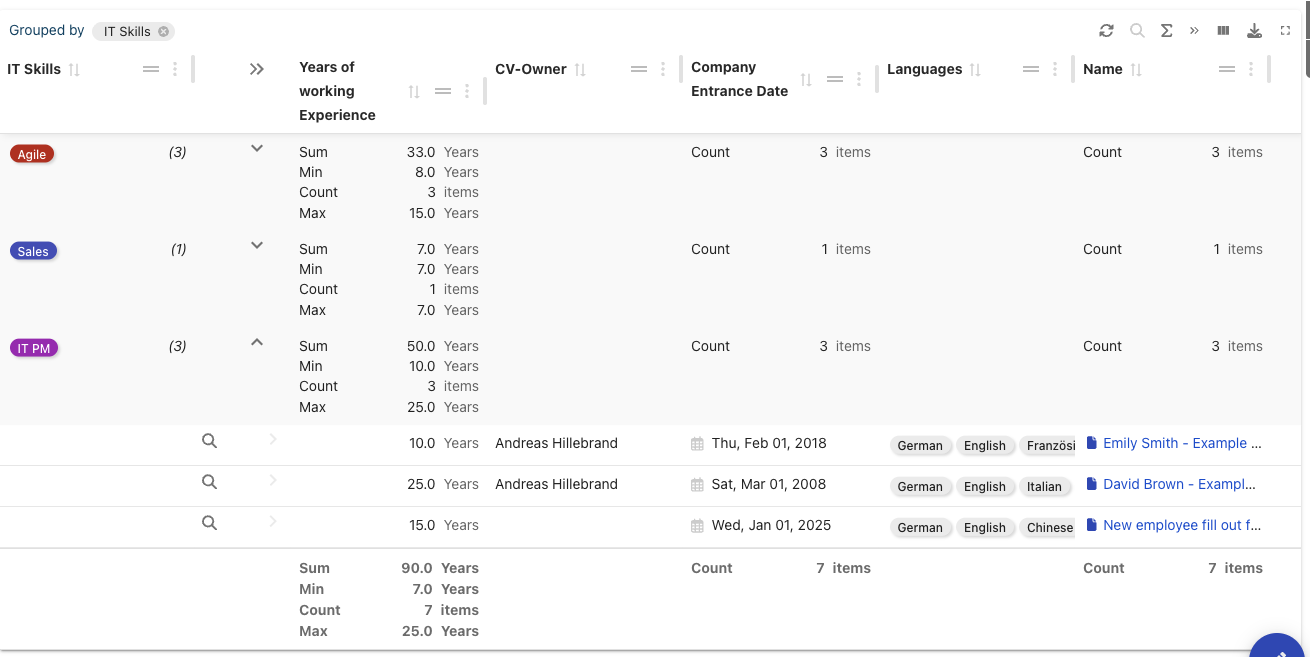
The mathematical functions will be performed for each group and for the total and you can collapse and expand each group to see individual values.